An Article “A living lab to develop smart home services for the residential welfare of older adults” has been published in the Technology in Society, Elsevier, 77, 102577, 2024
Hong, S., Jang, E., Cho, J., Lee, J., Rhee, J., Lee, H., Lee, M., Cha, S., Koo, C., Baik, O., and Heo, Y., A living lab to develop smart home services for the residential welfare of older adults, Technology in Society, Elsevier, 77, 102577, 2024 [SSCI, Q1, 0.5%].
Future Space Lab에서 [Technology in Society]에 새로운 논문을 게재하였습니다.
Abstract
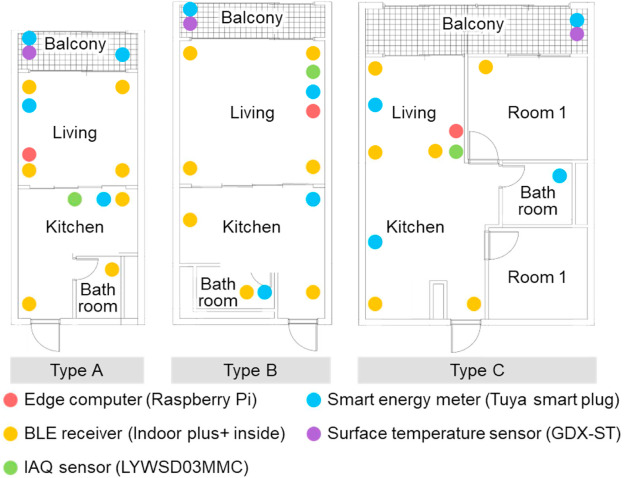
Owing to the decline in the physical and social functions of older adults, the residential environment substantially impacts the psychological and emotional stability and life satisfaction for older adults. Recently, there has been a growing interest in providing residential welfare services related to the health and independent living of the older adults. The primary objective of this research was to identify the needs and perceptions of older adults regarding smart home services and associated sensors and evaluate the indoor environment conditions of older adults through a living lab. Survey results indicate that older adults felt the burden of electricity bills in summer and winter and had relatively high safety-related smart home service needs. Focus group interviews with the participants in the living lab confirmed that older adults positively perceived the benefits and privacy of the living-lab sensors. In addition, the analysis of indoor environment data over one year from a case study household showed that approximately 66.4 % during the winter season and 13.1 % during the summer season have fallen within the neutral thermal comfort range according to the proposed approach (i.e., predicted mean vote (PMV) calculated using heart rate). This study adopted the proposed PMV method (hereafter PMV-P) that takes into account personal factors (e.g., metabolic rate of older adults that can be calculated using heart rate) and environmental factors (e.g., temperature, humidity) by using the real-time data collected from IoT (Internet of Things)-based sensors. Furthermore, this study proposed a new home energy management system (EMS) algorithm on the basis of model predictive control for reducing heating energy consumption while satisfying the thermal comfort. The new EMS was demonstrated to achieve 5–12 % heating energy savings depending on the thermal comfort preferences of occupants. Overall, the results of multidisciplinary research not only provided the preliminary evidence regarding the needs and perceptions of older adults toward IoT-based sensors but also showcased the development of IoT-based smart home service system through the living lab.
Comments
Post a Comment